International Economics Module 4 – The Dynamic Environment of International Trade
Assignment Help AUS is a highly acknowledged Homework Help provider among the students in Australia. We offer our Assignment Writing Help on more than 100 subjects with the assistance and guide of our highly knowledgeable and well-trained writers. Get the solution on Module 4 – The Dynamic Environment of International Trade Assignment instantly.
Learning Objectives
- The basis for the reestablishment of world trade following World War II
- The importance of balance-of-payment figures to a country’s economy
- The effects of protectionism on world trade
- The seven types of trade barriers
- The importance of GATT and the World Trade Organization
- Introduction to EU
- The emergence of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank Group
Introduction
- Proliferation of trade and emergence of the global economy
- Intensification of global competition
- More emerging markets
- Developments in technology allow communications with global consumers and movement of goods
World Trade and U.S. Multinationals
- Rapid growth of underdeveloped countries and new global marketing opportunities
- Rising living standards have created marketing opportunities for U.S. firms
- Resistance over domination of U.S. multinationals
- Expropriation and domestication of U.S. investments in Latin America
- In the Europe, U.S. multinationals were controlled tightly by protectionism laws
- Resurgence of competition from all over the world challenged the supremacy of American industry
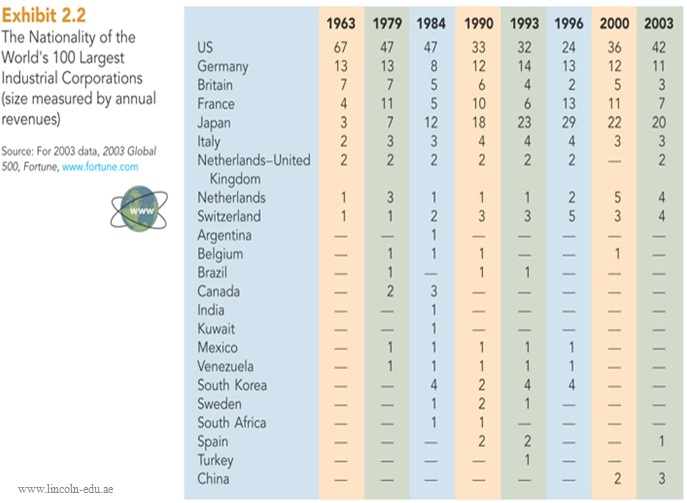
- Newly industrialized countries (NICs) such as Brazil, Mexico, South Korea, Taiwan, Singapore, and Hong Kong experienced rapid industrialization
- Economic power evenly distributed with growth of MNCs from other countries
- Establishment of the WTO
- Integration of European Union countries
- Creation of NAFTA, AFTA, and APEC
21st Century: The First Decade and Beyond
- With exception of China, slower economic growth in U.S. and other countries is currently evident.
- Faster growth rates expected in developing countries such as Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, and Russia.
- More trade expected in emerging markets, regional trade areas, and the established markets in Europe, Japan, and U.S.
- Companies need to be more efficient, improve productivity, expand global reach, and respond quickly.
- Greater growth in international sales expected by smaller firms.
Protectionism: Logic and Illogic
Countries use protectionist measures to shield a country’s markets from intrusion by foreign competition and imports.
Arguments for Protectionism include:
- maintain employment and reduce unemployment.
- increase of business size, and
- retaliation and bargaining.
- protection of the home market.
- need to keep money at home.
- encouragement of capital accumulation.
- maintenance of the standard of living and real wages.
- conservation of natural resources.
- protection of an infant industry
- industrialization of a low-wage nation
- national defense
Arguments 9-11 above are considered valid for protectionism
In general, protectionism contributes to industrial inefficiency and makes a nation uncompetitive
Protectionism is implemented through the imposition of trade barriers, which include tariff barriers and non-tariff barriers
Six Types of Non-Tariff Barriers
1. Specific Limitations on Trade:
- Quotas
- Import Licensing requirements
- Proportion restrictions of foreign to domestic goods (local content requirements)
- Minimum import price limits
- Embargoes
2. Customs and Administrative Entry Procedures:
- Valuation systems
- Antidumping practices
- Tariff classifications
- Documentation requirements
- Fees
3. Standards:
- Standard disparities
- Intergovernmental acceptances of testing methods and standards
- Packaging, labeling, and marking
4. Government Participation in Trade:
- Government procurement policies
- Export subsidies
- Countervailing duties
- Domestic assistance programs
5. Charges on imports:
- Prior import deposit subsidies
- Administrative fees
- Special supplementary duties
- Import credit discriminations
- Variable levies
- Border taxes
6. Others:
- Voluntary export restraints
- Orderly marketing agreements
Monetary Barriers
In addition to the Six Types of Non-Tariff Barriers, monetary barriers are also used by countries
Three types of monetary barriers include:
- Blocked currency: Blockage is accomplished by refusing to allow importers to exchange its national currency for the sellers’ currency.
- Differential exchange rates: It encourages the importation of goods the government deems desirable and discourages importation of goods the government does not want by adjusting the exchange rate. The exchange rate for importation of a desirable product is favorable and vice-versa
- Government approval: In countries where there is a severe shortage of foreign exchange, an exchange permit to import foreign goods is required from the government
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
1.GATT created as an agency to serve as watchdog over world trade and provide a process to reduce tariffs
2. GATT also provided a mechanism to resolve trade disputes bilaterally
3. GATT now replaced by the World Trade Organization
GATT covers three basic areas:
- trade shall be conducted on a nondiscriminatory basis;
- protection shall be afforded domestic industries through customs tariffs, not through such commercial measures as import quotas; and
- consultation shall be the primary method used to solve global trade problems.
World Trade Organization (WTO)
1. Unlike GATT, World Trade Organization is an institution, not an agreement
2. WTO provides a panel of experts to hear and rule on trade disputes between members, and, unlike GATT, issues binding decisions
European Union (EU) – Economic & Political Integration
European Union, 1993
positive integration – actively fostering integration
- Maastricht Treaty, 1992
- Amsterdam Treaty, 1997
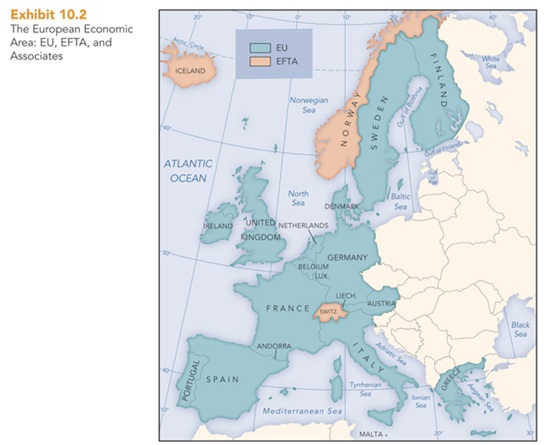
15 members currently
- Greece (1986), Spain (1986), Portugal (1986), Austria (1995), Finland (1995), Sweden (1995)
- 10 candidate countries (Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Estonia, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Hungary, Malta, Poland, Romania, Slovenia, Slovakia, Turkey)
European Union (EU) – Institutions
legislative – shared legislative powers
Council of the European Union
- ministers and heads of state of member countries
European Parliament
- direct election
executive – European Commission
- President and commissioners appointed by member states
- confirmed by European Parliament
judiciary – Court of Justice
European Union (EU) – Economic Integration
single market
- free movement of people, capital (investment), goods and services
monetary union
the Euro
- comes into existence January, 1999
- banknotes and coins in circulation, January 2002
- national banknotes and coins withdrawn from use (February 2002)
common labor market
- Schengen Agreement, 1985
European Union (EU) – Political Integration
political integration
- common political institutions
e.g. European Parliament
common European citizenship
- freedom of movements
- fundamental rights
- civil and political rights
common social citizenship (limited)
- access to social programs in other countries
common currency
- money traditionally symbol of sovereignty
- requires integrated monetary policy
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- Brunei
- Indonesia
- Laos
- Malaysia
- Myanmar
- Philippines
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Japan
- S. Korea
- China
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
- Australia
- Brunei
- Canada
- Chile
- China
- Hong Kong
- Indonesia
- Japan
- South Korea
- Malaysia
- Mexico
- New Zealand
- Papua New Guinea
- Peru
- Philippines
- Russia
- Singapore
- Taiwan
- Thailand
- U.S.A.
- Vietnam
North American Free-Trade Area (NAFTA)
- Canada
- United States
- Mexico
The International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- IMF was created to assist nations in becoming and remaining economically viable
- It assists countries that seek capital for economic development and restructuring
- IMF loans come with stipulations that borrowing countries slash spending and impose controls to curb inflation
- It helps maintain stability in the world financial markets
Objectives of the IMF include:
- stabilization of foreign exchange rates
- establish convertible currencies to facilitate international trade
- lend money to members in financial trouble
World Bank Group (WBG)
The goal of WBG is to reduce poverty and the improvement of living standards by promoting sustainable growth and investment in people.
The functions of the WBG include:
- lending money to countries to finance development projects in education, health, and infrastructure;
- providing assistance for projects to the poorest developing countries;
- lending directly to the private sector in developing countries with long-term loans, equity investments, and other financial assistance;
- provide investors with investment guarantees against “noncommercial risk,” so developing countries will attract FDI; and
- provide conciliation and arbitration of disputes between governments and foreign investors
Protests Against Global Institutions
In 1999 “anti-capitalist protestors” complained against the WTO, and IMF, over the unintended consequences of globalization that include:
- environmental concerns
- worker exploitation and domestic job losses
- cultural extinction
- higher oil prices, and
- diminished sovereignty of nations