BSBADV602 Develop an Advertising Campaign and BSBADV605 Evaluate Campaign Effectiveness Assignment
Is your Assignment work bothering you? Get the Assignment Writing Help from expert writers on BSBADV602 Develop an Advertising Campaign and BSBADV605 Evaluate Campaign Effectiveness Assignment Answers. We have Professional Assignment Writers who can solve your assignment homework before the deadline. We only hire PhD qualified writers with the intention that we can offer you the best and top quality work. We provide 100% unique work over 100+ subjects.
Assignment Details:-
- Topic: Advertising Campaign
- Words limit : 5500
ASSESSMENT 1 – Advertising concepts
Refer to Section 1 your Study Guide/ Power Point Presentation
Answer the following questions in your own words (50-100 words each)
1. Define the following terms:
- Industry
An industry is a group of companies that are related based on their primary business activities. In modern economies, there are dozens of industry classifications. Industry classification are typically grouped into larger categories called sectors.
Individual companies are generally classified into an industry based on their largest sources of revenue. For example, while an automobile manufacturer might have a financing division that contributes 10% to the firm’s overall revenue. the company would be classified in the automaker industry by most classification systems.
- Services
Services are essentially intangibles. Their purchase does not result in the ownership of anything physical. For example, you can only seek advice from the doctor, you cannot purchase him.
Services are all those economic activities that are intangible and imply an interaction to be realised between the service provider and the consumer.
Services are the separately identifiable, essentially intangible activities that provides satisfaction of wants, and are not necessarily linked to the sale of a product or another services.
- Products
Product represents the combination of all the features and benefits that you offer to your potential customers. It may include characteristics such as quality, packaging, after sales support and customer service. A product can be classified as tangible or intangible. A tangible product is a physical object that can be perceived by touch such as a building, vehicle, or gadget. Most goods are tangible products. For example, a soccer ball is a tangible product. An intangible product is a product that can only be perceived indirectly such as an insurance policy. Intangible data products can further be classified into virtual digital goods (“VDG”), which are virtually located on a computer OS and accessible to users as conventional file types, such as JPG and MP3 files. Virtual digital goods require further application processing or transformational work by programmers, so their use may be subject to license and or rights of digital transfer. On the other hand, real digital goods (“RDG”) may exist within the presentational elements of a data program independent of a conventional file type. Real digital goods are commonly viewed as 3-D objects or presentational items subject to user control or virtual transfer within the same visual media program platform. Services or ideas are intangible.
- Organisation
organisation is simply people working together for a common goal. It is a group of people assembling or congregating at one place and contributes their efforts to achieve a common goal. Hence, it is coordinates different activities for running the business enterprise efficiently so that the common goal can be achieved.
2. Explain the difference between ‘promotion’ and ‘place’ in the advertising mix.
Place refers to the sales and distribution of products and services in terms of the market where the product or t decision making starts with some sort of problem. The consumer develops a need or a want that they want to be satisfied. The consumer feel like something is missing and needs to address it to get back to feeling normal. If you can determine when your target demographic develops these needs or wants, it would be an ideal time to advertise to them. For example, they ran out of toothpaste and now they need to go to the store and get more.The next phase of the buying decision process begins when the customer starts looking for information that will help them solve their problem. They know they need something to fix their situation but aren’t sure which solution is best for them. The customer starts searching for information that will help him or her better understand their situation and identify what will fix their issues. At this point, the customer frequently turns to online research and conducts searches to find solutions.
service will be sold. How the product will sold or where the product will be sold for example selling in a physical location or through a online website. The distribution channel that available to sell retail, wholesale or intermediaries and agents and transportation or logistics that may be need.
Promotion refers to the promotional activities that you use to convey the benefits of your products and services to your target market in an attempt to persuade them to purchase it. Promotion includes a range of marketing methods including advertising, publicity, public relations, direct marketing, personal selling and sales promotions. Based on your organisation’s goals and budget, you need to identify the key promotional tools you would use to persuade your target market to buy your product.
3. What do you understand by ‘information advertisements’?
Information advertisements usually seek to introduce a new product or service to the market. These advertisements are used at the beginning of a product life cycle. They tell the consumer what the product is or what the product can do or where to find the product.
4. What is the purpose of ‘reminder advertising’?
Reminder advertising usually follows an extensive advertising campaign, and therefore does not elaborate on the reasons to buy the product. Common examples of reminder advertisements are those found on matchbooks and pencils and in skywriting, as well as the more traditional media vehicles.
It is also used for special events where the product gets linked to the special day as a reminder for people to buy the product for the special day. For example, you will notice that a number of companies start advertising their products just before Father’s Day to remind customers that they can buy their product as a gift for their father on Father’s Day.
5. Explain the first two stages of the consumer decision-making process in your own words?
t decision making starts with some sort of problem. The consumer develops a need or a want that they want to be satisfied. The consumer feel like something is missing and needs to address it to get back to feeling normal. If you can determine when your target demographic develops these needs or wants, it would be an ideal time to advertise to them. For example, they ran out of toothpaste and now they need to go to the store and get more.The next phase of the buying decision process begins when the customer starts looking for information that will help them solve their problem. They know they need something to fix their situation but aren’t sure which solution is best for them. The customer starts searching for information that will help him or her better understand their situation and identify what will fix their issues. At this point, the customer frequently turns to online research and conducts searches to find solutions.
6. Do you think the following ads are effective? Complete the questions in the table below
| ADVERTISEMENT | What is the purpose of the ad? | What product features is it highlighting? | Why is the ad effective? |
7. What factors would you need to consider when you advertise in different markets?
- Increasing sophistication of consumers
- Technological and electronic communication influences
- Buying behaviour in terms of personal, direct mail, electronic
- Geographical influences
- Consumer demands in regard to the environment
- Economic and employment influences, tighter markets, real disposable income
- Cultural and sub-culture
- Social trends
- Reference groups
- Social class
8. Anna Smith was looking for a mobile phone. She wanted to buy a phone that had a number of features, including sms, email, camera, video recorder etc. After doing a lot of research she decides to go to the Optus mobile store to buy the iPhone4S, as she has always used Apple products in the past. She goes in looking at the details of the iPhone 4S, which she had noted down on a piece of paper. She walks out of the store with a Samsung Galaxy mobile phone. Use the theory about consumer behaviour to explain:
- Why did Anna not follow through with her purchase decision to by an iPhone4S? What do you think happened? In your answer refer to the theory on the ‘Consumer decision making process’ (See Stage 4, Page 11 in your Study Guide)p
- What could Apple have done to make Anna purchase the IPhone4S at the store?
ASSESSMENT2 – Legislation and ethics
This assessment has 2 parts
Part A: Read the ‘Advertising and Selling’ guidelines published by the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) and answer the questions that follow
- What is the main Actand Schedulethat ensure that businesses trade fairly with consumers?
The Competition and Consumer Act 2010 No1
- Give TWO examples for each of the following in relation to advertising:
- Misleading or deceptive conduct
A fruit juice producer representing a product as being 100 per cent cranberry juice, when the product is 50 per cent orange juice.
A company representing that an international calling card has no fees, other than timed call charges, when in fact other fees are charged.
- Puffery
“Feels like you’re sleeping on a cloud.”“It’s a meal fit for a king.”“It’ll blow your mind away.”“World’s best coffee.”
“Red Bull gives you wings,” and it would be fair to say there is an implied understanding that drinking Red Bull won’t physically give you wings –
- Third line forcing
A travel agent offers certain flights to London on the condition that prospective passengers also acquire travel insurance from nominated insurance companies—that is, a prospective passenger will not be allowed to buy these flights (product 1) from the agent unless the passenger also buys the insurance (product 2) from a certain other business. A travel agent offers certain flights to London on the condition that prospective passengers also acquire travel insurance from nominated insurance companies—that is, a prospective passenger will not be allowed to buy these flights (product 1) from the agent unless the passenger also buys the insurance (product 2) from a certain other business.
A car dealer offers buyers a larger trade-in allowance on the condition that they obtain financing through a particular credit provider
- Is it legal for a travel agent to give a customer a free night stay at a holiday resort on the condition that they give the business the names of five of their friends and that these friends all buy their air tickets from the business? Why or why not? Refer to the specific legislation in your response.
Part B:
The company Roger David was asked to withdraw the advertisement shown below.
Also, the following advertisement -Oh, Lola! perfume advertisement, featuring Dakota Fanning, was banned in Britain but not Australia
Refer to the ‘AANA CODE FOR ADVERTISING & MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS TO CHILDREN; and answer the following questions:
- Do you think this advertisement is appropriate? Why or why not?
- Which section of the ‘AANA Code for advertising and marketing communications to children’ may have been breached by these advertisements? Explain the relevant breach in detail.
Refer to the ‘AANA 2012 CODE OF ETHICS- PRACTICE NOTE’ and answer the following questions - Are the above advertisements acceptable according to the AANA 2012 Code of Ethics- Practice Note’. Why or why not? Provide exact references from the Code
ASSESSMENT 3 – Develop an advertising campaign
This assessment has 3 parts
Part A:Theory questions
Refer to Section 3 and 4 in your Study Guide
- Explain the Hierarchy of Effects models (100 words approximately)
- What is the best media for reaching aged pensioners? Why?
- What are the three scheduling methods that are commonly used by advertisers?
- What methods of budgeting are used in small firms?
Part B: Develop an advertising campaign
Your task:
1. Read the advertising brief below
|
Advertising brief
Name of the company: Smith Soft Drinks Pty Ltd Product: Juicee (Fresh fruit juice) Background: Smith Soft Drinks Pty Ltd (SSD) is a fruit juice manufacturer that has been producing fresh fruit juice since 2002. SSD is based in Brisbane, Australia. It had successfully launched its fruit juices in 2003 and had become the Number 1 brand for fresh fruit juice in Queensland. Over the last 5 years, its sales have begun to decline as a number of alternative brands such as Boost and other smaller companies have flooded the market. Key issues
Define your message
Target audience
Perceived challenges
Budget
Campaign timing Commence within 6 weeks |
2. Develop an advertising campaign for the company (1000 words). Your advertising campaign must include the following:
1. Introduction(Write 3-4 sentences about Smith Soft Drinks and what they want you to do for them)
2. What are the key features of the product that you will highlight in your advertisements to attract the customers?
3. Research and write the names of at least 4 other juice companies that are well known in the market?
4. Target market
- What is the age group, gender, ethnic background, income etc of your target market?
- In which locations will you advertise ‘Juicee’? (What is the geographic area will you cover with your advertisements? Remember you have only $20,000 to spend)
- What are the usual activities or hobbies of your target group?
- What are the ‘needs’ of your target group?
5. Which media options will you use? Givedetails of where exactly the ad will be placed and why
6. How many times will you display the advertisement and why?
(Hint: Example: If you say that you will put your Ad on TV, you need to say when, which channel, and on which days of the week)
7. Will you produce the advertisements yourself or will you use a Creative and production service? Why or why not.
8. Timelines
- What will be the timeframe for the project?
- Are the 6 weeks allocated to the project realistic? Why or why not?
9. Advertising objectives using the DAGMAR model
- Hints:
- Objectives must be very specific
- How will you measure the effectiveness of the advertisement: How will the company feel that their $20,000 investment has returned good value for them? What will they get after spending $20,000 on your suggested advertisements?
| Objectives (be very specific)
What will your advertisement achieve? e.g My bill board advertisement outside the Logan Shopping centre will create awareness of the Juicee brand amongst 1000 people in the Logan area within 3 months |
What methods will you use to measure whether your advertisement has met its goal/ objective or not?
e.g I will do a quick survey of 2000 shoppers at Logan Shopping Centre after 3 months. If 50% can remember the name of Juicee, I’ll know that my campaign has been successful |
| My advertisement will … | |
| My advertisement will… | |
| My advertisement will… |
10. Develop an advertising Budget in the table below
(Use the sample advertising costs given below to plan and calculate all the costs for all the advertising activities)
SAMPLE ADVERTISING COSTS
Television advertising
- Prime time slots (5pm- 9pm): $6,000 for 30 seconds
- Other time slots: $3,000 for 30 seconds
Radio advertisements
- Prime time slots (7am- 9am and 3pm- 6pm): $2,000 for 30 seconds
- Other time slots: $1,000 for 30 seconds
Flyers (Printing and distribution)
- One page flyer (per 200 homes): $200
Google Ad Words
- Pay per click: $500- $1000 per month average costs
- Google Page 1: $5000 set-up fee plus $1000 per month (Starts becoming effective after 6 months)
| Advertising activity
(What type of advertising will you use?) |
Number of times/ number of spots
|
Total cost for the advertisement activity
AUD$
|
|
|
|
|
| TOTAL COST AUD$ | $ | |
11. Your evaluation strategy
- When and how will you measure the effectiveness of the ads?
- How will you make sure that your advertisements meet legal and ethical standards?
12. How will you pretest the ads?
13. How will you measure the effectiveness/resultsof the campaign?
ASSESSMENT 4 – Evaluating an advertising campaign
This assessment has 3 parts
Part A:Theory questions(Answer in 50 words each)
Refer to Section 6 in your Study Guide
- What are the benefits of testing the effectiveness of an advertising campaign
- What do you understand by laboratory tests?
- Explain any TWO methods of pretesting ads in your own words
- Explain any two methods of post testing ads in your own words
PART C: Evaluate the effectiveness of the campaign and make recommendations
Read the Telstra case study given below. Answer the questions that followbased on the case study
Telstra Case Study
Telstra has an advertising budget of $5 million per year. The Company’s current revenue is $200 million. Overall their goal is to increase their revenue to $220 million in one year.
In order to get started, the marketing team decided to first initiate two marketing activities in the next two months. The Team’s objective was to increase their revenue by $2million through these two activities.
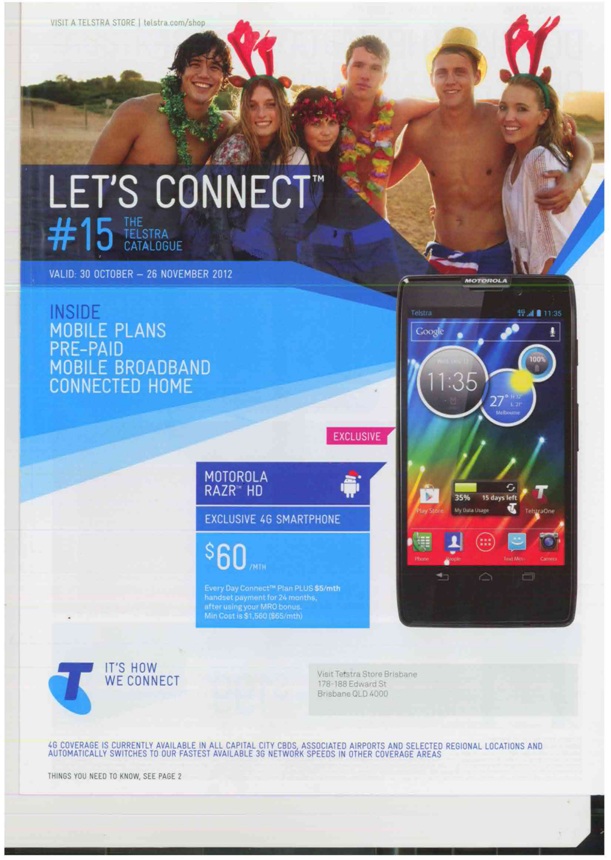
1. ACTIVITY 1:Design and distribute a catalogue, which would be distributed to homes in the 10 wealthiest suburbs in Brisbane. A copy of the catalogue is attached on the next page
Total cost:This activity cost them as follows:
*Printing of the catalogue. (50,000) $75,000
*Distribution of the catalogue. $15,000
*Radio advertisements on three radio stations for two weeks $30,000
*Hiring of staff at Call Centre to do follow-up calls $35,000
Total: $165,000
RESULT: This activity resulted in 1,205 new customers who signed up for the Telstra Mobile network @ $53 per month.
2. ACTIVITY 2: Television Campaign on Channels 9 and 10.
*TV advertisements for two weeks on channel 9 and 10 prime timeslots 5-8pm.
Total Cost: $650,000
RESULT:The television campaign resulted in 2,015 new customers who signed up for the Telstra Mobile network at $53 per month.
Here is a copy of the printed catalogue produced by Telstra
Answer the following questions based on the Telstra Case Study
- Calculate the total revenue that Telstra earned from the ‘Catalogue Campaign’?
- Calculate the total revenue that Telstra earned from the ‘Television Campaign’?
- Which campaign was more effective in terms of return on investment? Why?
- Did the marketing team meet their objectives for this campaign? Explain why or why not?
- Is the copy of the catalogue advertisement effective? Why or why not?
- If the marketing team wants to continue the advertising campaign, which advertising methods should they use more? Why?
- ADVERTISING CAMPAIGN
- What was Telstra’s revenue goal for the year? __________________
- How much revenue has Telstra already earned through the first two campaigns? ___________
- What was the advertising budget for the year? _________________
- How much money has already been spent on advertising? ______________________
- How much money is left over from the advertising budget? _____________________
- How much more revenue needs to be earned to achieve Telstra’s annual goal?________
- Develop an advertising campaign plan for Telstra for the future to achieve its overall goals
| Type of media | Describe your recommended advertising strategy for the future | How much will it cost?
(Use the actual costs from the earlier Telstra campaign to work out the costs) |
Expected outcomes
(How much revenue do you expect to get?) (Use the actual revenue from the earlier Telstra campaign to work out the potential revenue) |
| Catalogue |
|
||
| Television |
|
||
|
|
|||
| Radio
(Average cost is given below) · Prime time slots (7am- 9am and 3pm- 6pm): $2,000 for 30 seconds
· Other time slots:$1,000 for 30 seconds
|
|
||
| Web-based media
Google Costs (Example) · Pay per click: $500- $1000 per month average costs · Google Page 1: $5000 set-up fee plus $1000 per month (Starts becoming effective after 6 months)
|
|
||
| TOTAL |
- What are some of the goals that will be achieved by using your recommended strategies?
FOR REF… USE #getanswers2001514